If you want the highest level of cover available, then you will be best off opting for a fully comprehensive insurance policy.
These policies will cover you for more than any other standard insurance policy and they can often end up working out to be the best value for money on the market too.
In This Guide:
- What is fully comprehensive car insurance?
- What kind of cover can I expect?
- What isn't covered?
- Do I need fully comprehensive insurance?
- Is comprehensive car insurance more expensive than other types of cover?
What is fully comprehensive car insurance?
Fully comprehensive car insurance offers the highest level of cover out of the three types of car insurance available in the UK. The three levels of cover you can get are:
- Third party: covers you for any damage caused to another person, their vehicles or property.
- Third party, fire & theft: also covers your own vehicle if it is stolen or damaged by fire.
- Fully comprehensive: covers everything that third party, fire & theft insurance covers, but also covers damage caused to your own vehicle, even if you were at fault for the accident.
What kind of cover can I expect?
A fully comprehensive car insurance policy will come with all of the accident and third party-liability cover than you can expect from any standard policy. However, where most policies will only cover certain personal items like mobile phones or sat nav systems against accidental (e.g. fire) damage and theft, with a fully comprehensive policy, your whole car will be covered.
Some of the things you should be typically covered for with a fully comprehensive car insurance policy include:
- Any damage caused to a third party, their vehicle or property.
- Theft or vandalism of your car.
- Any damage caused to your own car by a fire or accident.
- Personal injuries caused by a road accident.
The following are commonly included in fully comprehensive car insurance policies, but may have to be added as an extra:
- Breakdown Cover: Provides you with roadside assistance should your car break down whilst driving.
- Windscreen Cover: covers the cost of replacing cracked and chipped windscreens.
- Legal Protection: covers the cost any legal expenses that arise from making a car insurance claim, or if a claim is made against you.
- Personal Belongings Cover: protects your personal possessions from theft while left in your car, including sat-navs and phones.
What isn't covered?
Fully comprehensive insurance may offer the highest level of cover you can get with a car insurance policy, that doesn’t mean will cover absolutely everything. There are many things you should watch out for that typically won’t be covered by any car insurance policies. These include:
- Driving under the influence: If you’re involved in an accident but were found to be under the influence of drink or drugs whilst driving, then your car insurance will be invalidated, and you won’t be able to claim. You also risk points on your licence, a criminal conviction and even jail time, so don’t even think about it.
- Poor security: If you’re found to have been careless when it comes to keeping your car secure, you’re also unlikely to receive a payout from your insurer. For example, if your car has been stolen but you left it unlocked with the windows open, then don’t expect to be covered.
- Invalid driving licence: Driving without a valid licence will likely invalidate your car insurance policy and can also lead to prosecution.
- Wear and tear: the general upkeep and maintenance of your car is your own responsibility. Most insurers won’t pay out to cover repairs on general wear and tear.
- Wrong fuel cover: most car insurance policies won’t cover you if you damage your car by putting in the wrong type of fuel. However, some insurers may allow you to include wrong fuel cover, also called misfuelling cover, as an add-on.
- Driving other cars: fully comprehensive insurance policies won’t usually allow you to drive other people’s cars. Some will, however, but will typically only be for short-term use and emergencies.
As with any other kind of car insurance policy, the specifics of the cover will depend on the provider, so you should always read the small print to make sure that you’re getting exactly what you need.
Do I need fully comprehensive insurance?
While it is a legal requirement to be insured to drive on UK roads, it is up to you as to what level of cover you get. Third party policies won’t cover the cost of repairing your own vehicle should you need after an accident. Fully comprehensive insurance offers the highest level of cover available, so will give you peace of mind knowing you’re financially protected should anything happen on the road.
Is comprehensive car insurance more expensive than other types of cover?
Not always. Because a comprehensive policy covers for more eventualities, you'd expect them to always be more expensive when all other factors are the same. However, in some cases insurers take into account the fact that high risk drivers are more likely to take out less comprehensive policies, so it's possible for a fully comprehensive policy to be less expensive than a third party policy.
This means that in high-risk categories, such as young drivers, fully comprehensive policies can sometimes be found at cheaper rates.
In fact, we found that customers looking for fully comprehensive cover were offered cheaper annual premiums than any others: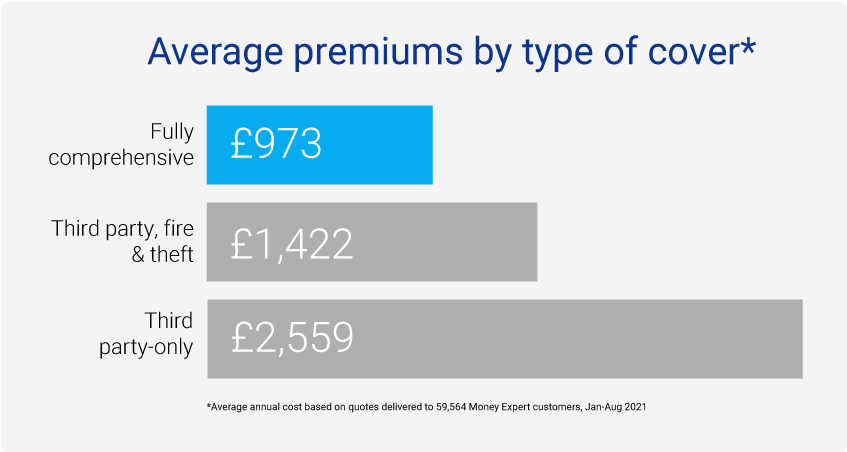
Fully comprehensive: £973
Third party, fire and theft: £1,422
Third party-only: £2,559
Frequently asked questions
Which type of car insurance is cheapest?
Is comprehensive better than third party insurance?
It's all about deciding the level of risk you're willing to take on not having to make a claim. For most people, the peace of mind of knowing they're covered for more eventualities is more valuable than the savings on a less comprehensive policy.
Can I change my comprehensive insurance to third party?
Generally, however, there's no harm in asking. If you're a loyal customer, your insurer might be willing to change your policy in order to keep you on for subsequent years.
Which company is best for comprehensive car insurance?
For this reason, the wisest move is to always use a car insurance comparison tool to find the best deal for you, as this can change year on year, when you buy a new car or when you make a claim.
Is full coverage the same as comprehensive insurance?
The term “full coverage” is not commonly used in insurance policies in the UK.




